Production of various high-end fabrics reaches 7 million meters annually, including a wide range of fashionable new products and exquisite items, with a broad coverage of color patterns.
How Does Coated Dyed Cloth Handle Wear and Tear Over Time?
2025-09-05
Coated dyed cloth is widely used across industries ranging from fashion and upholstery to outdoor gear and industrial applications. Its popularity stems from its unique combination of aesthetic appeal, durability, and functional properties. Unlike standard dyed fabrics, coated dyed cloth undergoes additional treatments that enhance its resistance to wear, environmental stress, and daily use. Understanding how it withstands wear and tear over time is essential for buyers, designers, and manufacturers who aim to maximize both the longevity and performance of the fabric.
What Is Coated Dyed Cloth?
Before discussing wear and tear, it is important to understand what coated dyed cloth actually is. In simple terms, this type of fabric starts with a base textile, such as cotton, polyester, or nylon, which is dyed to achieve the desired color. After dyeing, the fabric is treated with a coating that can be made from materials like polyurethane, acrylic, silicone, or other polymers. This coating forms a thin protective layer on the surface of the cloth, altering its texture, sheen, and functional properties.
The coating may serve multiple purposes:
- Water resistance: Prevents moisture from penetrating the fibers.
- Stain resistance: Makes it easier to wipe off spills and dirt.
- Enhanced strength: Adds structural support to reduce fraying and tearing.
- UV resistance: Protects the color and fabric integrity under sunlight.
Different coatings and application methods lead to variations in durability, flexibility, and appearance, which in turn affect how the fabric handles wear and tear over time.
Factors Affecting Wear and Tear
The durability of coated dyed cloth is influenced by several factors. Understanding these can help users predict performance and make informed choices.
1. Type of Base Fabric
The underlying textile plays a significant role in determining durability. Natural fibers like cotton are breathable and comfortable but may show wear more quickly if not reinforced. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon are inherently more resistant to abrasion, stretching, and moisture, making them better candidates for coated applications.
2. Coating Material
Different coatings provide varying levels of protection. For instance:
- Polyurethane coatings offer excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but may degrade under prolonged UV exposure.
- Acrylic coatings are generally more rigid, providing strong protection against stains and wear but can crack over time if the fabric is bent repeatedly.
- Silicone coatings combine flexibility with weather resistance, making them suitable for outdoor fabrics.
The choice of coating directly affects how well the fabric can handle daily use and environmental stress.
3. Coating Thickness
Thicker coatings generally provide better protection against scratches, abrasions, and spills. However, excessive thickness can reduce flexibility and make the fabric feel stiffer. Balancing thickness and comfort is key to achieving long-term durability.
4. Fabric Weave and Construction
The weave of the fabric—whether plain, twill, satin, or knit—affects its mechanical strength. Tightly woven fabrics resist fraying and tearing better, while looser weaves may be more prone to abrasion. When coated, the weave’s resilience is further enhanced, but the coating’s adherence is critical to maintaining strength.
5. Usage Conditions
How the fabric is used has a significant impact on wear and tear. High-traffic applications, such as upholstery or outdoor gear, expose the fabric to constant friction, stretching, and environmental stress. Frequent exposure to sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations can accelerate coating degradation. Conversely, fabrics used in low-stress settings will generally retain their properties for longer periods.
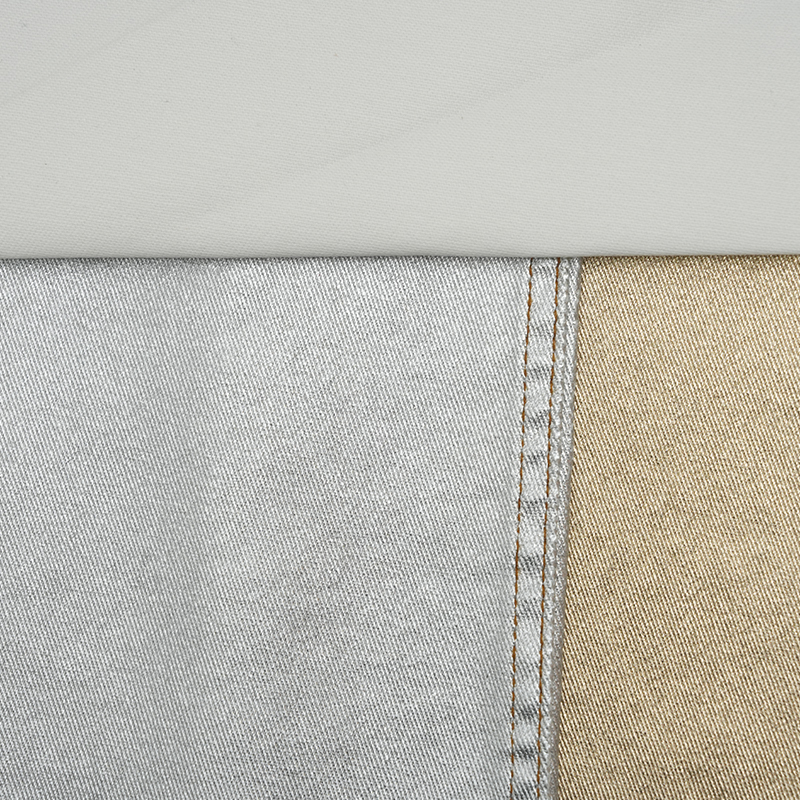

Mechanisms of Wear in Coated Dyed Cloth
Wear and tear in coated dyed cloth can manifest in several ways. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain how and why the fabric changes over time.
1. Abrasion
Abrasion occurs when the fabric surface rubs against another material. Coatings act as a protective barrier, reducing friction between fibers and external surfaces. Over time, repeated abrasion can wear down the coating, eventually exposing the base fabric. The extent of abrasion resistance depends on both the coating material and thickness.
2. Cracking and Peeling
Some coatings, particularly rigid ones, may develop cracks or peel when the fabric is flexed repeatedly. This is more common in fabrics used for outdoor applications, bags, or apparel where bending and folding are frequent. Properly formulated coatings balance flexibility with durability to minimize this type of wear.
3. Fading
Dye fading is another form of wear, particularly in fabrics exposed to sunlight or harsh cleaning agents. High-quality coatings can act as UV barriers, slowing down color degradation and preserving the aesthetic appearance of the fabric.
4. Fraying and Fiber Weakening
Even with coatings, the base fibers can gradually weaken due to mechanical stress, moisture absorption, or chemical exposure. Coatings generally slow this process by reducing direct contact between the fibers and abrasive elements. However, prolonged wear and improper care can still lead to fraying at edges or seams.
5. Staining and Contamination
One of the functional advantages of coated dyed cloth is improved resistance to stains and contamination. While spills are easier to wipe off, repeated exposure to harsh chemicals or oils can gradually compromise the coating, allowing stains to penetrate the fabric over time.
Testing and Measuring Durability
Manufacturers and quality control teams often assess coated dyed cloth using standardized tests to predict how well it will withstand wear and tear. Common methods include:
- Martindale abrasion test: Measures resistance to rubbing and abrasion by simulating repeated friction.
- Tensile strength test: Evaluates the force required to stretch or tear the fabric.
- Pilling resistance test: Assesses the formation of small fiber balls on the surface.
- Water and stain repellency tests: Determine how well the coating prevents penetration of liquids.
- UV aging test: Measures color retention and coating stability under prolonged sunlight exposure.
These tests provide useful benchmarks for estimating fabric longevity under real-world conditions.
Maintenance and Care for Longevity
Proper care is crucial for extending the life of coated dyed cloth. Recommendations include:
- Gentle cleaning: Use mild detergents and avoid harsh chemicals that can degrade coatings.
- Avoid excessive heat: High-temperature washing or ironing can damage coatings.
- Store in a cool, dry place: Moisture and sunlight can accelerate wear.
- Minimize friction: Rotate cushions or apparel to prevent localized abrasion.
- Repair minor damage: Promptly fixing small cracks or tears can prevent further deterioration.
Regular maintenance significantly enhances the fabric’s ability to withstand wear over time.
Applications Where Durability Matters
The ability of coated dyed cloth to resist wear makes it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Outdoor gear: Tents, jackets, and backpacks require abrasion and water resistance.
- Upholstery: Furniture and automotive seats benefit from stain and wear protection.
- Industrial fabrics: Protective clothing, tarpaulins, and conveyor belts require high mechanical strength.
- Fashion accessories: Handbags and footwear benefit from coatings that resist scratches and stains.
In each application, selecting the right combination of base fabric, coating type, and maintenance routine is key to maximizing durability.
Conclusion
Coated dyed cloth is engineered to handle wear and tear better than standard fabrics, thanks to its protective surface layer. Its performance over time depends on multiple factors, including the base fabric, coating material, thickness, weave, and usage conditions. Common forms of wear include abrasion, cracking, fading, fraying, and staining, all of which can be mitigated with proper fabric selection, care, and maintenance.
Understanding these factors allows users to make informed decisions, ensuring that coated dyed cloth retains its appearance, functionality, and structural integrity for years. Whether for outdoor gear, furniture, industrial applications, or fashion, coated dyed cloth offers a durable and versatile solution for environments where wear and tear are inevitable.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt