Production of various high-end fabrics reaches 7 million meters annually, including a wide range of fashionable new products and exquisite items, with a broad coverage of color patterns.
How Does Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth Differ from Pure Cotton Fabric?
2025-11-07
When selecting fabrics for clothing, bedding, or home textiles, understanding the subtle differences between materials is key to making informed choices. Two popular options often compared are Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth and pure cotton fabric. While both fabrics share certain characteristics, they also have distinct properties that influence comfort, durability, appearance, and care.
Understanding the Basics
Pure cotton fabric is made entirely from cotton fibers harvested from the cotton plant. It has been a staple textile material for centuries, appreciated for its softness, breathability, and natural feel. Cotton fabric is versatile, used in clothing, bed linens, towels, and upholstery.
Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth, on the other hand, is a blend of cotton fibers and modal, a type of semi-synthetic fiber derived from beechwood pulp. Modal is known for its silky texture, smoothness, and enhanced moisture absorption compared to regular cotton. When combined with cotton, it creates a fabric that retains the natural qualities of cotton while benefiting from the advanced characteristics of modal. The “dyed” aspect refers to the fabric undergoing a coloring process, which can influence texture, vibrancy, and colorfastness.
Fiber Composition and Feel
One of the most noticeable differences between Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth and pure cotton fabric lies in fiber composition. Pure cotton contains 100% natural cotton fibers. Its texture is soft but may feel slightly coarse depending on the cotton grade, thread count, and weave.
Modal-cotton blends, however, contain a mix—commonly around 50-70% modal and the remainder cotton, though ratios vary. Modal fibers are smoother, more uniform, and have a silk-like feel. This combination results in a fabric that feels softer and drapes more fluidly than standard cotton. The hand feel of modal-cotton is often described as luxurious, even when the cotton component is of standard quality.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Breathability is a hallmark of cotton fabric. It allows air circulation, making it suitable for warm climates or active wear. Pure cotton absorbs moisture efficiently, helping keep the skin dry to some extent. However, cotton can retain water for longer periods, which may make it feel damp and heavy when wet.
Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth generally has superior moisture management due to modal fibers’ higher absorbency. Modal can absorb water up to 50% more than cotton without feeling wet. This makes modal-cotton blends ideal for garments like underwear, T-shirts, and sportswear where quick moisture absorption and drying are desirable. Additionally, the blend prevents excessive shrinkage and improves comfort after washing.
Durability and Strength
Durability is another key factor distinguishing these fabrics. Pure cotton is strong and resilient, but it can lose shape or wear out faster when subjected to frequent washing or friction. Cotton fibers may shrink, wrinkle, or fade over time, especially if washed in hot water or exposed to harsh detergents.
Adding modal to cotton enhances fabric strength. Modal fibers are resistant to shrinking, pilling, and fading. Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth maintains its shape and appearance longer than pure cotton, particularly after repeated washes. While both fabrics are durable, the blend offers extended longevity, making it a practical choice for everyday clothing and frequently used textiles.
Color and Dye Retention
Color vibrancy and retention is an area where differences are noticeable. Pure cotton fabric readily absorbs dyes, but colors may fade more quickly, particularly with exposure to sunlight or repeated laundering. Cotton’s natural fiber structure can make it challenging to achieve consistently deep or uniform coloration without specialized dyeing techniques.
Modal fibers, however, absorb dyes efficiently, producing brighter, more uniform colors. Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth often exhibits richer, longer-lasting hues than pure cotton. The smooth fiber surface also contributes to a softer and shinier appearance, giving garments a slightly more polished or luxurious look.
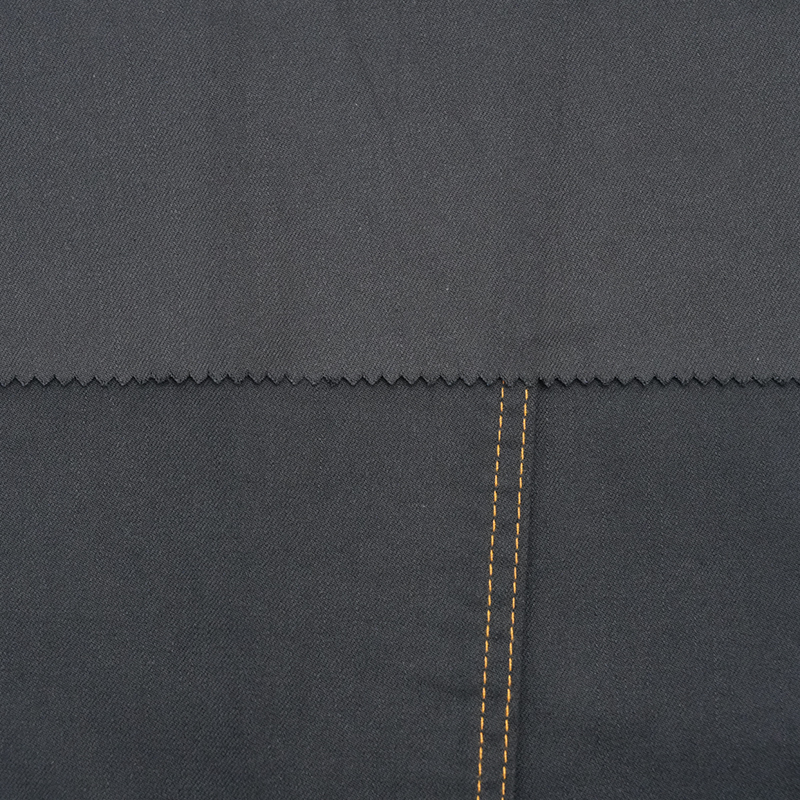

Wrinkle Resistance and Maintenance
Maintenance requirements can differ significantly between the two fabrics. Pure cotton wrinkles easily due to its natural fiber structure. Ironing may be required to maintain a crisp appearance, and shrinkage is common if washed improperly.
Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth is naturally more wrinkle-resistant. Modal fibers allow the fabric to retain shape and smoothness after washing, reducing the need for ironing. Blending cotton with modal also helps control shrinkage, making the fabric more forgiving during laundering and suitable for easy-care clothing.
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is increasingly relevant when choosing fabrics. Pure cotton is a renewable natural fiber, but conventional cotton cultivation can require significant water, pesticides, and fertilizers. Organic cotton reduces these impacts, but costs may be higher.
Modal, derived from beechwood, is often produced in a closed-loop process, meaning chemicals used in fiber production are largely recovered and reused. This makes modal relatively environmentally friendly compared to other synthetic fibers. A modal-cotton blend can combine the natural qualities of cotton with the eco-conscious aspects of modal, though the blend is not entirely natural.
Applications and Suitability
Both fabrics have their specific applications:
- Pure Cotton Fabric: Ideal for traditional clothing, casual wear, bed linens, towels, and items where breathability and natural texture are priorities. Its simplicity and natural feel make it a classic choice.
- Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth: Preferred for garments requiring a soft hand feel, gentle draping, and enhanced color retention. It is commonly used in T-shirts, undergarments, activewear, and high-quality home textiles. The fabric’s resistance to shrinkage and wrinkles makes it convenient for everyday use.
Cost Considerations
Price is another factor. Pure cotton is widely available and cost-effective, particularly in standard grades. High-thread-count cotton fabrics, however, can be expensive. Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth usually carries a higher price due to the added production complexity of blending fibers and dyeing processes. Nevertheless, the higher initial investment can be justified by longer-lasting wear and reduced maintenance needs.
Conclusion
In summary, Modal-cotton Dyed Cloth and pure cotton fabric share the comfort and natural appeal of cotton, but differ in several practical ways:
- Texture and Feel: Modal-cotton is softer, smoother, and more luxurious.
- Moisture Management: Modal-cotton absorbs water more efficiently, keeping it dry and comfortable.
- Durability: Modal-cotton resists shrinkage, fading, and wear better than pure cotton.
- Color Vibrancy: Modal-cotton holds dye more evenly and for longer periods.
- Wrinkle Resistance: Modal-cotton requires less ironing and maintains shape better.
- Environmental Impact: Both have sustainable options, with modal production offering a closed-loop advantage.
- Applications: Pure cotton is versatile and traditional, while modal-cotton excels in garments requiring softness, durability, and color retention.
Choosing between these fabrics depends on priorities such as comfort, appearance, maintenance, and longevity. For everyday wear and traditional items, pure cotton remains a reliable and natural choice. For enhanced softness, drape, and color stability, modal-cotton Dyed Cloth offers a practical and aesthetically appealing alternative. Understanding these distinctions allows consumers and textile professionals to select fabrics that best meet their functional and stylistic needs.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt